Probablistic Technology
Comparison Chart
How much time and money do companies spend agonizing over decisions because they cannot afford to pay for mistakes—or worse yet, how many times do they fail to make a timely decision or even to make a decision altogether?
All too frequently a decision is based only on a gut feeling, a hunch, a temporary fix, the status quo, or the application of some arbitrary safety factor. In an increasingly competitive marketplace, today’s companies should be very uncomfortable with such uncertain approaches to decision-making and the often unexpected and damaging results.
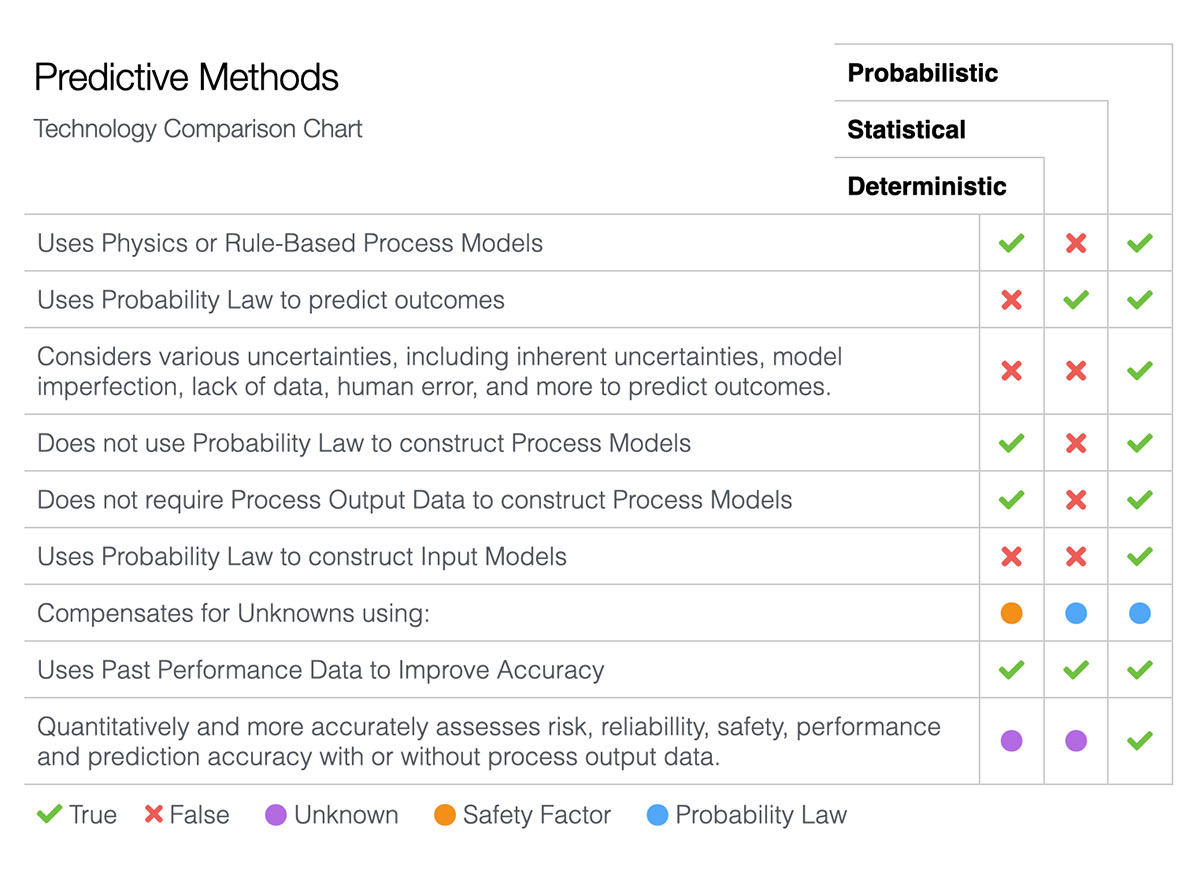
Until very recently, most technical and business decisions, even those using the popular Six-Sigma process, were based on either deterministic or statistical approaches—i.e., either focusing strictly on the physical characteristics of a process and making arbitrary corrections, or focusing only on interpretation of pure statistical data that may be flawed or difficult to obtain. Both approaches compound their own inherent problems, as they fail to consider effects of uncertainty.
In contrast, Probabilistic Technology considers both the physical and statistical aspects of a process while systematically accounting for various types of uncertainties including inherent uncertainties, model imperfection, lack of data, measurement error, human error, decision uncertainties, human intervention, and more.
In this way, Probabilistic Technology succeeds where the deterministic and statistical approaches fail — yielding the best, most accurate results and leading to efficient, cost-effective solutions.
Across industries worldwide, companies are rapidly discovering the advantages of understanding how variation and uncertainties can impact their products and are using this knowledge to outdistance the competition. The use of Probabilistic Technology has become the key to this process for many industries.